
A microbiological analyzer is a tool that helps people in microbiology. It makes it easier to check for bacteria, fungi, and other small organisms. Scientists use this machine to test samples. They find out what microorganisms are in them. Every microbiological analyzer can test samples fast. This helps labs do their microbiology work. In microbiology labs, workers use these machines to check for germs in blood, food, and water. A microbiological analyzer gives quick test results. This makes it important for microbiology. People trust a microbiological analyzer to test many samples. It helps keep people safe.
A microbiological analyzer makes microbiology tests faster and more correct. These machines are very important in many test steps.
Key Takeaways
Microbiological analyzers help labs find germs fast. They check samples like blood, food, and water. This helps labs work quicker and with fewer mistakes. These machines use smart tools like AI, lasers, and sensors. They can spot many kinds of microbes at the same time. This saves time and makes test results better. They are very important in hospitals and food safety. They also help with checking the environment. They give fast and trusted results. This keeps people safe and stops outbreaks. Automation in these analyzers lowers human mistakes. It lets labs test many samples at once. This helps labs give faster answers and safer results. Quality control rules make sure every test is right. This makes microbiological analyzers important for safe and good testing.
Microbiological Analyzer Overview

Main Function
A microbiological analyzer helps scientists and lab workers find tiny living things. These machines make work in microbiology labs faster and more correct. The main job of a microbiological analyzer is to test for pathogens in samples. It can find, count, and help name bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms.
Modern analyzers use smart tools like AI, digital pictures, and strong microscopes. These tools let the analyzer see single microbial cells and give results fast. The analyzer can also use machine learning to sort microbes with high accuracy. This makes finding infections much quicker than old ways. In the past, culture tests could take up to 14 days. Now, a microbiological analyzer can finish the same test much faster.
Microbiological analyzers make data better by automating how results are captured and checked. They also keep digital records, which helps labs follow rules and stay safe.
The analyzer can find pathogens that do not grow in normal lab cultures. This is important for finding and treating sickness. The analyzer also helps count how many pathogens are in a sample. This information is important for patient care, food safety, and the environment.
Key Applications
Microbiological analyzers are used in many places. Their main uses include:
Clinical Diagnostics:
Hospitals and clinics use microbiological analyzers to test blood, urine, spit, and tissue. These tests help find pathogens that cause sickness like pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract infections. Fast results mean doctors can start treatment sooner. The analyzer also checks for antibiotic resistance, which helps doctors choose the best care.Food Safety:
Food companies use these analyzers to test for pathogens like Salmonella and E. coli. This testing keeps food safe and helps companies follow food safety rules. Quick finding of harmful microbes stops foodborne illness and keeps people healthy.Environmental Monitoring:
Scientists use microbiological analyzers to test water, dirt, air, and surfaces. These tests help find pathogens that can cause outbreaks or hurt the environment. For example, testing water for E. coli keeps drinking water safe. The analyzer also checks air in buildings for mold or fungi.Supporting Trends:
New technology, like AI and the Internet of Things (IoT), makes microbiological analyzers even better. These tools let labs watch tests in real time and share data from far away. AI helps find pathogens faster, while IoT lets labs see results from anywhere.
Microbiological analyzers have many good points over old ways. They give faster and more correct results. They also help labs follow rules made by groups like AOAC INTERNATIONAL, which sets standards for food and clinical testing. These analyzers help with quality control and show labs use the best methods.
Microbiological analyzers change how pathogens are found and diagnosed. They make testing in labs more trustworthy, quick, and safe for everyone.
Analyzer Components
Sample Handling
A microbiological analyzer begins with sample handling. The machine gets samples from blood, food, or water. Lab workers put each sample in a special container. Robotic arms move the sample to the right place. This keeps the sample clean for testing. The analyzer can work with many samples at once. Labs can do more tests in less time. Each sample goes through steps to get ready for detection. The machine mixes, heats, or cools the sample if needed. Good sample handling helps every test give correct results.
Careful sample handling keeps germs out. This step is important for good testing.
Detection Technologies
Detection technologies help the analyzer find microbes in samples. The machine uses light, chemicals, or sensors to find bacteria and fungi. Some analyzers use lasers to look for microbial cells. Others use color changes to show a positive test. The analyzer can do many kinds of tests, like checking for Salmonella or E. coli. Each method works quickly and gives clear answers. The machine can test for many pathogens at once. This saves time and helps labs finish tests fast.
Detection Method | What It Finds | Speed |
|---|---|---|
Light Sensors | Bacteria | Fast |
Chemical Tests | Fungi | Medium |
Lasers | Microbial Cells | Fast |
Data Processing
Data processing is the last part in the analyzer. The machine gathers results from each test. Computers check the data for mistakes. The analyzer sorts results and makes simple reports. Lab workers use these reports to see if a sample has harmful microbes. The machine keeps all test data safe. This helps labs keep track of tests over time. Data processing also helps labs follow safety rules. The analyzer can send results to doctors, food safety teams, or experts.
Fast data processing lets labs share results quickly. This helps keep people safe from microbes.
Microbial Identification Methods
Microbiological analyzers use different ways to find microbes. These ways help labs find germs fast and correctly. Each way has special benefits for finding and testing.
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry, like MALDI-TOF MS, changed how labs find microbes. This way uses lasers to make protein patterns from each germ. The analyzer matches these patterns to a big library. Scientists can find bacteria, fungi, and viruses at many levels. MALDI-TOF MS works much faster than old ways. It can test many samples at the same time, so each test costs less. This technology also helps stop mistakes and slowdowns. Labs use mass spectrometry to find lots of germs in clinical, food, and environmental samples.
MALDI-TOF MS gives quick and trusted results. It is a top pick for finding germs in labs today.
Biochemical Assays
Biochemical assays are still important for finding microbes. These tests use chemicals to see how germs react. The analyzer checks for color changes or other signals. Each germ has its own reaction pattern. Labs use these patterns to know which microbe is there. Biochemical assays work well for everyday tests. They help labs find germs in blood, food, or water. The tests are simple and give clear answers. Many analyzers use biochemical assays with other ways for better results.
Molecular Techniques
Molecular techniques make finding germs faster and more exact. PCR and multiplex PCR let labs find many germs in one test. These ways help labs find more germs and make tests better. Next-generation sequencing finds germs and resistance genes in hard samples. For example, 16S rRNA gene sequencing helps when cultures do not work. Microfluidic systems and Raman spectroscopy can find single bacteria without culture. These ways help labs find germs in tough samples and make tests more trusted.
Technique | Benefit | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
PCR | Finds many germs | Severe pneumonia cases |
Multiplex PCR | Finds many germs at once | Food safety tests |
NGS | Finds many types of germs | Cancer patient samples |
Raman Spectroscopy | Finds single bacteria | Environmental monitoring |
Molecular techniques help labs find germs fast, even in samples with lots of microbes.
Microbiological analyzers use these ways together for quick, correct, and trusted results. This helps labs keep people safe from germs and make tests better.
Diagnostic Microbiology in Practice
Automation Benefits
Automation is changing how labs do diagnostic microbiology. Machines now do many testing steps, like getting samples ready and making diagnoses. This means people make fewer mistakes. Labs can test more samples each day. Automated systems are built to be easy to use. They follow rules like ISO 9241 and FDA guidance. These rules help new workers avoid errors. Machine learning helps the analyzer sort hard data. It gives quick and correct results. These changes let labs give answers faster and with fewer mistakes. Automation lets labs test lots of samples at once. This helps doctors find out what is wrong sooner and helps patients get care faster.
Automated diagnostic microbiology systems help labs work faster and make fewer mistakes, leading to better diagnosis and safer results.
Quality Control
Quality control is very important in microbiology testing. Labs use standards like McFarland to make sure tests are right. The McFarland Standard sets how cloudy a bacterial sample should look. This helps labs use the same amount of bacteria in every test. When labs use this standard, they can trust their results. The standard uses chemicals to match real bacterial samples. Labs check each sample with this standard before testing. This step keeps test results correct and the same every time. Good quality control helps labs find germs and make the right diagnosis.
Clinical and Food Safety Uses
Diagnostic microbiology is important for both hospitals and food safety. In hospitals, labs use analyzers to test blood, urine, and tissue for germs. Fast results help doctors treat patients quickly. In food safety, labs test for bad bacteria like E. coli and Salmonella. These tests make sure food is safe and help stop outbreaks.
Role in Food Safety Monitoring and Outbreak Prevention | |
|---|---|
Microbiological Testing | Finds pathogens in food, checks cleaning and cooking, stops outbreaks |
HACCP | Watches key points to stop hazards |
Chemical Checks | Looks for harmful chemicals |
Allergen Management | Stops allergic reactions |
Temperature Monitoring | Keeps food at safe temperatures |
Microbiology analyzers also help check the environment. They use indicator organisms to see if cleaning works and to find problems early. This keeps people safe by stopping germs from spreading.
Microbiological analyzers are very important in labs today. These machines help workers finish tests fast and with good accuracy. Advanced AI models, like 1D-CNN, work really well for diagnosis and testing. The table below shows how these models make tests more correct and efficient.
Model | R² (Total Dataset) | RMSE | MAPE% | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1D-CNN | 0.9983 | 0.0519 | 0.37 | Highest accuracy for test and diagnosis |
EL | 0.9982 | Higher | Higher | Strong for diagnosis and test |
ANN | >0.997 | Moderate | <0.6 | Robust for test and diagnosis |
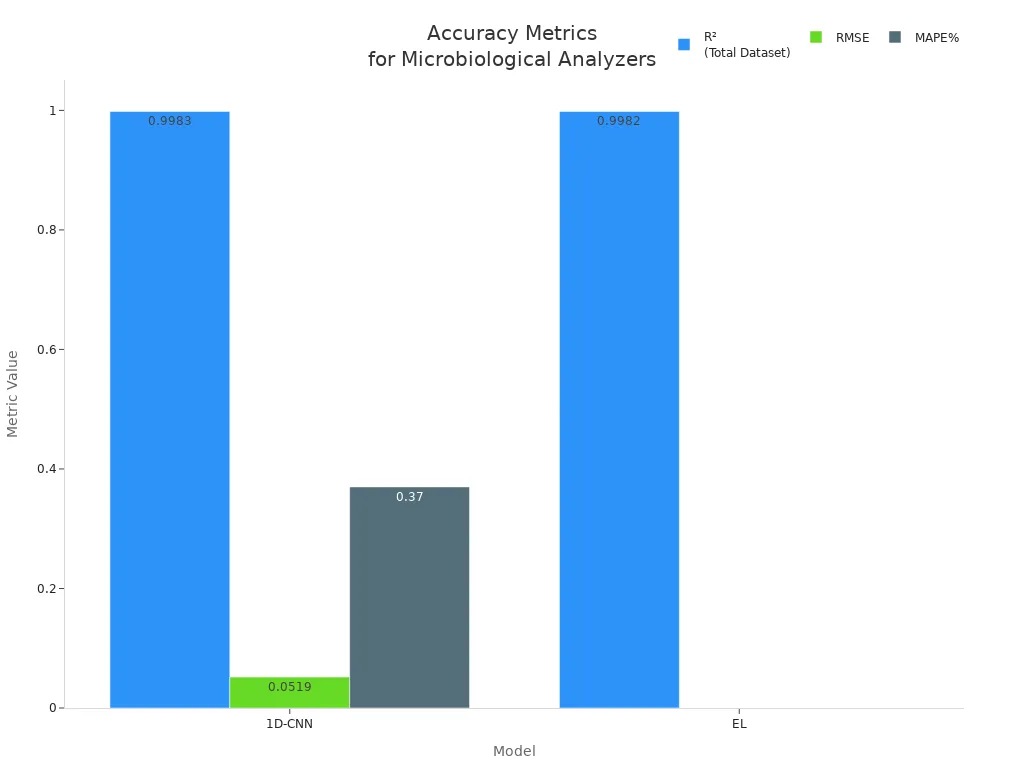
These machines make tests and diagnoses more trustworthy. They help keep people, food, and the environment safe. Labs can count on these analyzers to make every test better.
FAQ
What does a microbiological analyzer do in a laboratory?
A microbiological analyzer helps lab workers do tests fast. The machine finds, counts, and tells what germs are in samples. It gives quick results for each test. This helps doctors and food safety teams decide what to do.
How does automation improve the test process?
Automation lets the analyzer do many steps by itself. The machine gets samples ready, runs tests, and checks results. This makes tests faster and helps stop mistakes.
Can the analyzer test for more than one germ at a time?
Yes, the analyzer can check for many germs in one sample. It uses special tools to look for bacteria, fungi, and viruses together. This saves time and helps labs finish tests quickly.
Why is quality control important in every test?
Quality control checks if each test works the right way. Labs use rules to make sure every test is correct. This helps labs trust the results and keeps people safe.
Where do people use these analyzers for testing?
People use these analyzers in hospitals, food labs, and water plants. Each place needs to check samples for germs. The analyzer helps labs finish tests fast and with good results.
https://www.schinstrument.com/microbiological-analyzer-what-it-is-and-how-it-operates.html





